
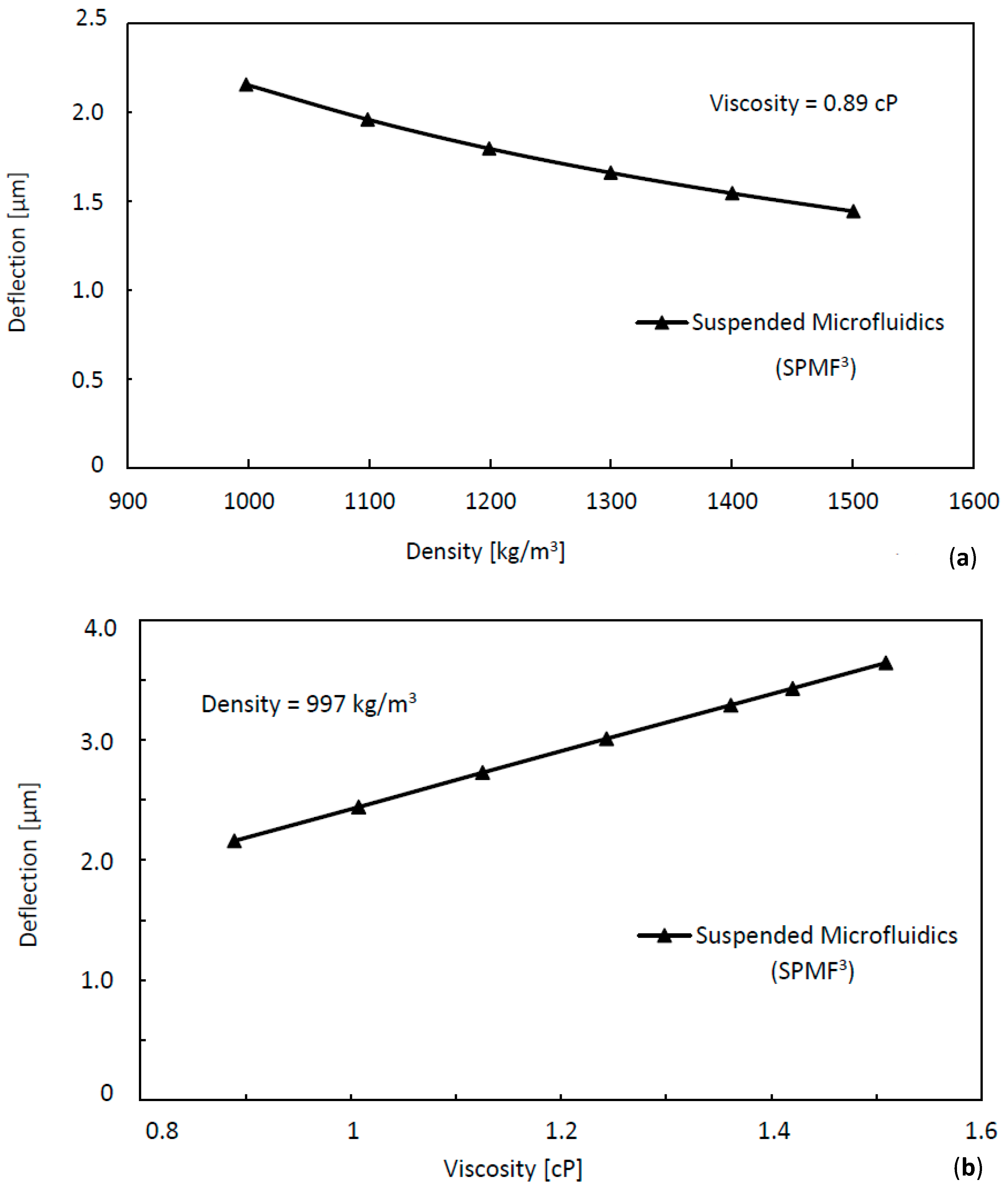
They may be the same size, but the steel cube weighs more than the ice cube. Think about an ice cube and a cube of steel. Dynamic (cP) / Density = Kinematic (cSt)įor a given sample, with a density greater than one, dynamic viscosity will always be the higher number.ĭensity is the ratio of the mass (or weight) of the sample divided by the volume of the sample.Kinematic (cSt) x Density = Dynamic (cP).Density actually provides a way to convert between a kinematic and a dynamic viscosity measurement. The unit of measure of kinematic viscosity is Centistokes (cSt).Ī basic difference between the dynamic and kinematic viscosity measurements is density. The time is converted directly to kinematic viscosity using a calibration constant provided for the specific tube. There are several ways to find the kinematic viscosity of a fluid, but the most common method is determining the time it takes a fluid to flow through a capillary tube. Put another way, kinematic viscosity is the measure of a fluid’s inherent resistance to flow when no external force, except gravity, is acting on it. The other way is to measure the resistive flow of a fluid under the weight of gravity. One way is to measure a fluid’s resistance to flow when an external force is applied. Water at 20 ☌ has a kinematic viscosity of about 1 cSt. Other units are: 1 St ( Stoke) = 1 cm 2/s = 10 −4 m 2/s. The SI unit of the kinematic viscosity is m 2/s. The kinematic viscosity is the ratio between the dynamic viscosity and the density of a fluid.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
